Hi everyone, welcome to Electrical Maker, Today we are going to discuss what is the solar cell.
What is the solar cell?
In this article, we will understand what is the solar cell and how a solar cell works, its advantages, disadvantages, and its application.
Introduction about What is the Solar Cell
A solar cell is a P-N junction device that converts solar energy into electrical energy. The basic unit block of a solar cell consists of two or more specially designed layers of semiconductor materials processed with an additive cause that causes the device to become Photosensitive.
When the photons strike the surface of the solar cell then the electron-hole pairs are released, generating a flow of electric current.
Thus a solar cell is a transducer that converts the solar radiation directly into electricity.
The efficiency of conversion of solar energy into electrical energy depends upon many factors such as the reflectivity of the surface, Absorption factor of the material, rate of generation, and recombination of charge carriers.
In the case of solar cells, various types of semiconductor materials are used such as GaAs, CdSe, etc but the most common semiconductor material used is silicon. About 90% of the solar cells are composed of silicon.
It is a reciprocal device of a LED. A solar cell is actually a large Photodiode designed to work solely as a photovoltaic device and used to give as much output power as possible.
Solar cell Construction
A Solar cell consists of a semiconductor (silicon or GaAs) p-n junction diode packed with a glass window on the top.
The top surface consists of an extremely thin layer of P-type material or silicon having a thickness in the range of 0.002 inches to 0.006 inches. This layer is extremely thin so that this layer can emit electrons when subjected to light rays.
On the top face of the P-layer, the metal finger electrodes are prepared so that light can get enough space between fingers to reach the junction.
There is a nickel-plated ring the silicon layer is present which is the positive output terminal. The button plating present is the negative output terminal.
The solar cell produced commercially is available in flat strip form for the efficient coverage of available surface areas.
How Solar Cell Work
Solar Cell works on the principle of photovoltaic effect. The photovoltaic effect is the process of generation of EMF due to the absorption of ionizing radiation.
When two pieces of semiconductor material (silicon) containing N-type and P-type impurities are connected by some means then a P-N junction is created.
The photons of light energy are absorbed by this junction then the free electrons of N- region will tends to flow towards the P-region and the holes of the P-region will tend to move towards the N-region to compensate for their respective deficiencies.
Due to this diffusion, an electric field (Ef) is created from the N- side to the P- side.
If an electrical contact is made with the two semiconductor materials and the contacts are connected through an external load resistance then the free electrons will flow from the N-type region through the resistance to the P-type region.
Here the free electrons will enter the holes and become bounded electrons thus both free electrons and holes will be removed.
When the flow of electrons through the external resistance takes place then it will constitute an electric current which will continue as long as more free electrons and holes are formed by the solar radiation. Thus in this way solar energy is converted into electrical energy.
The amount of electric current produced will depend on the intensity of the solar radiation and the surface area of the cell receiving the radiation. The dimension of the silicon cells is approximately 10 cm by 10 cm.
V-I Characteristic of a Solar cell
The graph between the voltage and current is called the V-I characteristic of the solar cells. The graph of the solar cells is shown below.
Solar cells have three operating conditions such as open circuit condition and short circuit condition.
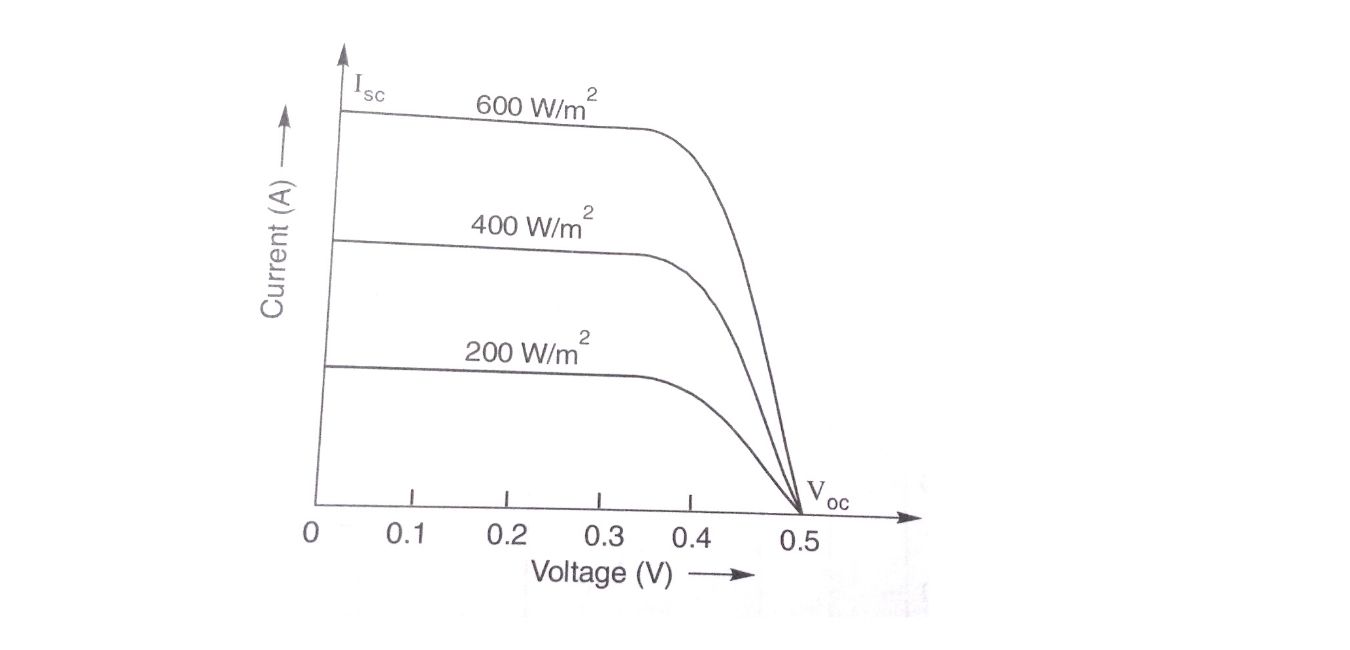
Open circuit condition – Open circuit condition means when P- terminal and N- terminal of the solar cell is open or we can say that the external resistance is very high in the order of megaohms. In the case of silicon open circuit voltage is about 0.5v.
Here in the case of the open circuit, no current will flow between the terminal and only open circuit voltage is present which is VOC denoted in the graph.
Short circuit condition– When external resistance is short-circuited then the terminal voltage will be zero and the current flows between the terminals will be maximum called short circuit current ISC.
The graph between points B and C is almost flat hence solar cell is called a constant current source.
Types of Solar Cells
Solar cells on the basis of type of crystal are classified into three types.
|
|
|
Monocrystalline silicon cells
- In this silicon cell, silicon is doped with boron to produce p-type semiconductors.
- Monocrystalline rods are extracted from silicon and then sawed into thin plates or wafers.
- The wafer’s upper layer is doped with phosphorus to produce an N-type semiconductor and this becomes a P-N junction.
- The maximum efficiency of this type is 24%.
Polycrystalline silicon cells
- Here in this silicon cell, liquid silicon is poured into blocks that are sawed into plates.
- Crystal structures of varying sizes are formed during solidification.
- The size of the crystallites mainly depends upon the cooling condition.
- If the molten silicon is cooled very slowly then the crystallites obtained are of larger size.
- Polycrystalline silicon cells are lower in cost.
- The maximum efficiency of this type of silicon cell is 17.8%.
Amorphous Silicon cell
- When a silicon film is deposited on glass or other substrate material then this is called an amorphous silicon cell or thin layer cell.
- Since the thickness of the layer here is less than 1μm so the production cost is lower due to the cost of the material.
- This type is primarily used in low-power equipment such as pocket calculators, watches, etc.
- The maximum efficiency of this type of silicon cell is 13%.
| S.NO | Types of solar Cell | Band Gap | Maximum Efficiency |
| 1. | Monocrystalline silicon cell | 1.12 ev | 24% |
| 2. | Polycrystalline silicon cell | 1.12 ev | 17.8% |
| 3. | Amorphous Silicon cell | 1.75 ev | 13% |
Solar cell advantages
- It is a renewable source of energy.
- It directly converts solar energy to electrical energy.
- Easy operation.
- In long term, it is economical in power generation.
- It is environment friendly.
- It is pollution-free.
- It is useful in rural, remote areas and satellites.
- No fuel is required for its operation.
- Solar cells have a longer life (15 to 30 years).
- These are suitable for a mobile load such as car busses, etc.
Solar cell disadvantages
- Its initial installation cost is high.
- Dependency of power generation on the season (Power generation is lower in the rainy season).
- Requirement of sunlight for its operation.
- Requirement of larger space for high power application.
- Lower efficiency.
- Also, its efficiency may degrade with time.
- Solar cell performance depends on geographical location.
- For storage, a battery is required.
- As the solar cell is a DC source so for AC appliances operation there is a need for an inverter.
- Its operation can be performed in the daytime only.
Solar cell applications
- Solar cells are used in artificial satellites and in space probes like Mars orbiters.
- It is also used in traffic signals, calculators, and toys.
- Used in rural telephone exchange operation.
- Used in wireless transmission systems or TV relay stations in remote areas.
- Used for battery charging.
- Now a day’s solar photovoltaic system is also used in street lighting.
- Useful for Pumping of water for drinking and irrigation.
I hope you like this article on what is the solar cell?. For any doubt and suggestions please comment in the comment section below.
