Contents
What are Nuclear Power Plants?
Let’s start a new article about Nuclear power plants?. In this article, first, we will discuss the introduction of what are nuclear power plants and then the construction and working of nuclear power plants and after that merits and demerits of nuclear power plant.
Introduction
A nuclear power plant is a type of power plant in which atomic energy is used to generate electricity by converting atomic energy into useful power. In a nuclear power plant, heat produced by the reactor is used to drive a turbine and the turbine is connected to a generator that produces electricity.
The nuclear power plant is different from a steam power plant and a hydroelectric power plant, as nothing is burned to produce steam. In this power plant, the uranium atom gets split to get the energy to generate electricity.
The electricity demand is increasing rapidly worldwide. So the need for energy in the future will also increase and this future energy need energy can only be fulfilled by the nuclear power source as the reserve of fossil fuels like coal, gas, and oil are depleting at a faster rate.
So there is a need to move towards an alternative source of energy, and at the current time, nuclear power is the only alternative source that can fulfill the future energy demand of the world.
Selection of site for Nuclear Power Station
- Availability of water – The site selected must be nearer to a water source, such as a river or lake. A sufficient amount of water is required for cooling purposes. Here, the amount of water required is more than twice the water required for a thermal power plant of the same size.
- Disposal of waste – Waste produced by the process of nuclear fission in nuclear power plants is radioactive in nature so it must be disposed properly to avoid any health hazards.
- Distance from populated areas – The site selected for the nuclear power station should be quite away from the populated areas from the point of view of safety as there is a danger of the presence of radioactivity in the atmosphere near the nuclear power plant.
- Nearness to load center – These types of plants should be located as near to the load center as possible, consistent with safety considerations, to reduce the cost of transmission.
- Transportation facilities – Transportation facilities are required only during the construction stage of the nuclear power plant, as very little fuel is required in this power plant.
- Type of Land- The land required in this power plant must have a surface strong enough to support the heavy reactor.
Construction of a Nuclear Power Plant
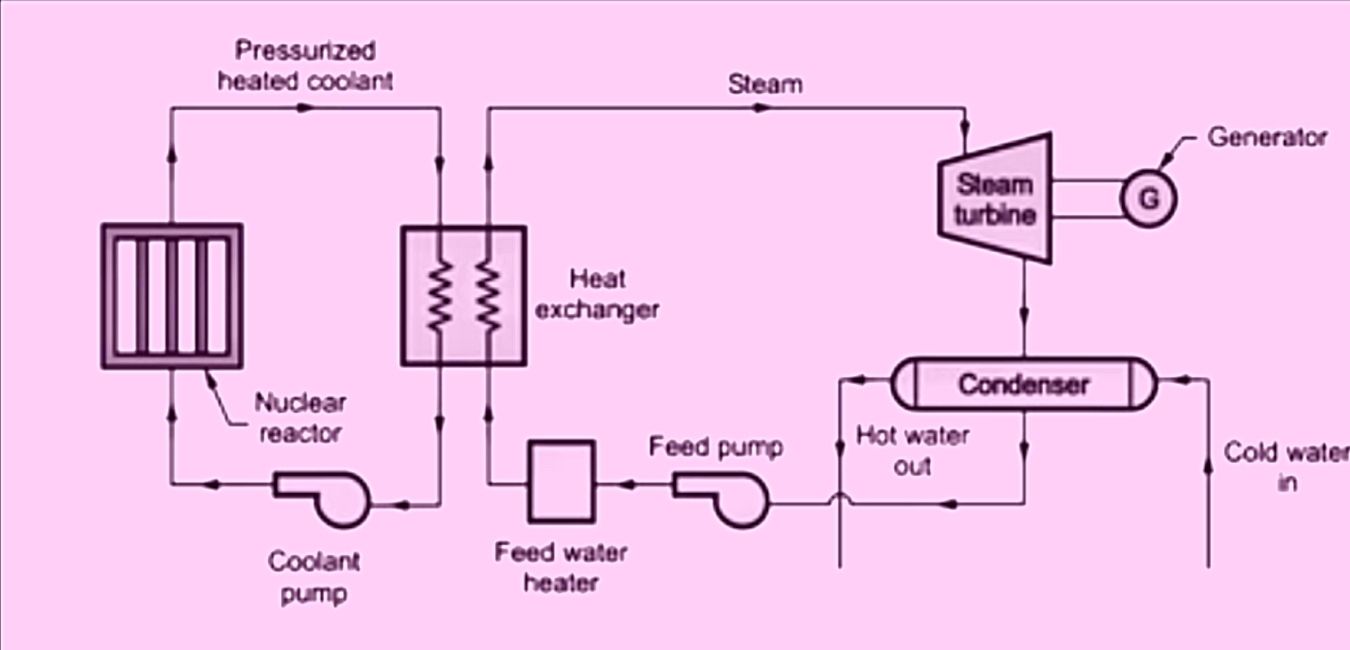
A nuclear power plant consists of a nuclear reactor (for heat generation), Heat exchanger (for converting water into steam using the heat generated in the nuclear reactor), Alternator, Steam turbine, Condenser, Exciter, etc.
Nuclear Reactor
A nuclear reactor is considered the most important part of this power plant because in this part main chain reaction takes place, and due to this chain reaction huge amount of energy produced in the form of heat.
This generated a large amount of heat produced in which nuclear reactor is used to generate steam and run the turbine to generate electricity. The main function of a nuclear reactor is to control the emission and absorption of neutrons.
A nuclear reactor consists of various elements such as Fuel, moderators, Control rod, coolant, reflector, shield, etc.
Fuel
Uranium-235 (U235) and Plutonium -239 (Pu239) are generally used as fuel in the nuclear reactor of the power plant. Naturally obtained uranium contains 99.23 % of 92U238 and the remaining 0.77 % is of 92U235. These radioactive elements are used in nuclear reactors as fuel.
Nuclear fission is the process used in nuclear power plants for the generation of energy. In the process of nuclear fission, an atom of a heavy element is bombarded with a neutron as a result heavy elements get slipts into lighter elements and a large amount of energy is released.
Fission reaction example of U235
U235 + 1 Neutron = Lanthanum148 +Br80+ 3 free electrons + 200Mev energy
Moderator
The kinetic energy of the neutrons produced by the fission process is very high and these electrons are termed as fast neutrons. So the purpose of the moderator is to reduce the energy level of the neutrons so that the chain reaction may not result in an accident.
Heavy water (D2O) is an ideal moderating material used in many reactors in spite of its heavy cost. Other various types of moderators used in nuclear reactors are Graphite, Beryllium, Boron, and lithium.
Control Rods
Control rods are the rods that are inserted into the nuclear reactor core from the top of the reactor vessel. Control rods are used to initiate the chain reaction and to maintain a steady-state value during the operation of the nuclear reactor.
Under any emergency conditions, the nuclear fission process can be automatically shut down with the help of control rods. These rods control the fissioning in the nuclear reactor by absorbing the excess neutrons available.
Therefore the materials used for control rods must have a high absorption capacity for neutrons. The most commonly used material for control rods is cadmium, boron, and helium because these materials have very high neutrons absorbing capacity.
Coolant
Coolant is the medium through which the heat generated in the nuclear reactor is transferred to the heat exchanger. Coolant flows through and around the reactor core. Coolant helps in maintaining the interior of the reactor at the desired temperature.
Various types of material used as coolants are as follows,
The liquid used as coolant – Ordinary and heavy water.
Gases used as coolant- Air, H2, CO2, and Helium.
Metals as a coolant- Molten lithium and sodium.
Reflector
It completely surrounds the reactor core within the thermal shielding arrangement and helps to bounce escaping the neutrons back into the core. This helps in conserving the fuel as the low-speed neutrons return and thus helps in maintaining the chain reaction. It is generally made up of the same material as the moderator.
Shielding
The whole nuclear reactor is enclosed in lead, iron, or concrete shields so that no fast neutrons, slow neutrons, beta particles, etc. can escape or leak, as these particle rays are very harmful to human beings. Shielding is generally made of concrete, lead, or iron.
The nuclear reactors used in Nuclear power plants are of various types such as Advanced Gas-Cooled reactor, Pressurised Water reactor, Magnox reactor, Boiling water reactor, Liquid Metal reactor, and Fast Breeder reactor.
Advanced Gas Cooled Reactor (AGR)
This type of reactor uses uranium dioxide as fuel and CO2 as coolant, which passes through the heat exchanger and raises steam. For moderator AGR uses graphite.
Advanced Gas Cooled reactor can be refueled even on load and this is an operational advantage of this reactor. This reactor is economical when the load factor is more than 75%. The overall efficiency of AGR is about 40%.
Pressurized Water Reactor
The fuel used in this type of reactor is enriched uranium oxide. Here pressurized water is used as a coolant as well as a moderator. The overall efficiency of a pressurized water reactor is about 33%.
Magnox Reactor
In this reactor natural uranium is used as fuel. Magnox reactor is also a type of gas-cooled reactor and similar to Advanced Gas-Cooled reactor. Also in this reactor CO2 is used as a coolant and for moderator, graphite is used.
In this reactor, the fuel element is connected to a special magnesium alloy called Magnox. For this reactor overall efficiency is about 30%.
Boiling Water Reactor (BWR)
This reactor also uses enriched uranium oxide as fuel. In this reactor for coolant and moderator ordinary water is used. The overall efficiency of this reactor is about 33%.
BWR is a direct cycle reactor as the steam is generated in the reactor itself and this steam after passing through the turbine and condenser returns to the reactor.
Liquid Metal Fuelled Reactor
In this reactor liquid metal, fuel is used i.e uranium in sodium. Sodium is used as a coolant and graphite is used as a moderator. This reactor is also called a sodium graphite reactor.
Fast Breeder Reactor
A fast breeder reactor is a vessel in which the necessary quantity of enriched uranium or plutonium is kept without a moderator. This reactor is different from thermal reactors because a thermal reactor uses fissile nuclear fuel and produce heat.
Whereas a fast breeder reactor produces heat and at the same time converts fertile material into fissile material. In this reactor, we can convert uranium-238(U238) to Plutonium-239(Pu239) or Th232 in U233. So in this reactor, we can make Plutonium from depleted Uranium.
For this reactor is also possible to produce more fissile material than it consumes.
Breeding Ratio- It is the ratio of the number of secondary fuel atoms produced to the number of primary fuel atoms consumed. The breeding ratio is always greater than or equal to 1.
Heat Exchanger
It is used to convert the water into steam by using the heat generated in the reactor. The coolant provides heat to the heat exchanger and this heat is utilized in raising the steam. And after giving the heat the coolant is again fed to the reactor.
Steam Turbine
The steam produced in the heat exchanger is provided to the steam turbine and in the steam turbine the steam expands due to which the turbine rotates to generate electricity and after doing this steam is exhausted to the condenser.
Condenser
It is used to condense the steam coming out of the steam turbine. The condenser condenses the steam into the water, which circulates into the heat exchanger to form steam.
Alternator or Generator
It is connected with the steam turbine through a shaft. When the steam turbine drives the alternator then it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy and thus generates electricity. The output from the alternator is delivered to the bus bar through a transformer, circuit breaker, and isolators.
Working of a Nuclear Power Plant
The nuclear power plant uses the process of nuclear fission to generate energy. In the process of nuclear fission nucleus of atoms having larger atomic weight gets split into atoms of lower atomic weight and a large amount of energy is produced.
The huge amount of energy that is produced during the process of nuclear fission is used to convert the water into steam and the generated steam is used to drive the steam turbine through which an alternator is coupled.
When the steam turbine rotates then the alternator coupled with the steam turbine also rotates and thus mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy. Thus in this way electricity is produced through a nuclear power plant.
Merits of Nuclear Power Plant
- A nuclear power plant requires less space as compared to any other type of power plant of equal size.
- A nuclear power plant requires a very small amount of fuel. So there is a saving in the transportation cost of the fuel.
- The operation of nuclear power plants is more reliable.
- This power plant does not get affected by weather conditions.
- The fuel used in this power plant can be recycled.
- The nuclear power plant is most suited to meet large power demands.
- The running cost is lower.
Demerits of Nuclear Power Plant
- The capital cost of a nuclear power plant is always higher than other power plants.
- It is not suitable for varying loads as reactors can’t be easily controlled.
- In this power plant, there is always a danger of radioactivity.
- The disposal of radioactive products is a big problem.
- The maintenance cost is high.
- This power plant is hazardous to the workers.
- Its operation requires well-trained workers.
I hope you like this post on nuclear power plants. For more topics related to electrical and electronics engineering, click on the link given below.

Jitu Kumar is the Founder and Senior Content Head of Electrical Maker. On electricalmaker.com, we publish the latest educational updates regarding Engineering.
